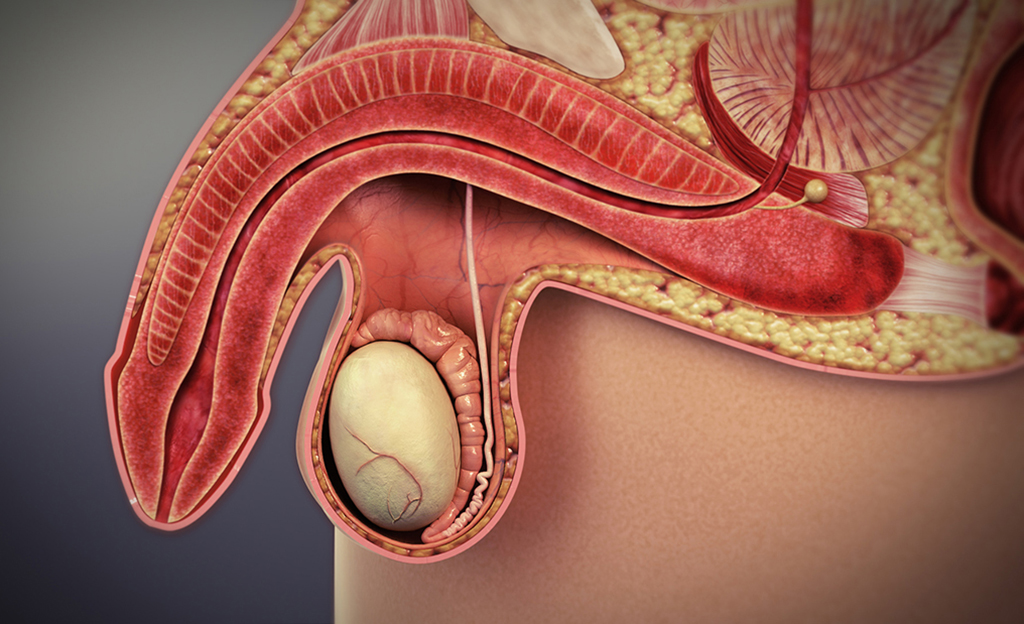
There are several definitions but most frequently ED is referred to as the inability to achieve or maintain an erection long enough to complete intercourse.
Also called sexual dysfunction, erectile dysfunction (ED) is known as one of the more common forms of medical conditions that can affect men’s sexual performance. An astonishing fact: estimates show between 15 and 30 million Americans currently suffer from some form of erection problems.
A number of different things can cause these kinds of erection problems, but the most common include excessive stress, recreational or prescription drug use, liver disease (usually from alcoholism), or even from a penile implant that isn’t working properly.
Most of the causes are in fact physical rather than psychological, to begin with, but some estimates show up to 70% have a psychological component as well – erection problems can be crushing to a man’s self-image.
Here we’ll show you some of the risk factors involved with this problem, how the condition is diagnosed, and how the many men master the problem – the solutions that work.
Common Causes:
For most men, impotence comes from one of a number of fairly common sources.
Oftentimes it is common medicines (typically those for blood pressure, antidepressants, and appetite suppressants) that may cause ED as a side effect.
There are also potential psychological effects that can come from stress, guilt, anxiety, fear, depression, fear of sexual failure, and low self-esteem. These influences can account for as much as 20 % of cases on their own but are also usually contributors to the other 80% of cases. It is safe to say that once a man begins to have problems, his fears and concerns usually add to the problem.
It’s a well-known fact that excessive alcohol use and smoking also cause cardiovascular problems that can lead to lowered testosterone and ED.
Any time there is an injury to the spine or pelvis (or cancer surgery on the prostate or bladder) there can be damage to the nerves near the penis that may lead to problems with erections in the future.
Damaged nerves and tissues (smooth muscles, arteries, etc.) are the most common source of problems. Diabetes, kidney disease, excessive alcohol use, and conditions like multiple sclerosis and atherosclerosis account for the majority of cases of impotence. Up to 50% of men with diabetes experience sexual problems at some point.
Although aging is associated with erection problems, it is not ‘just a part of getting older. It is caused by other health issues that affect greater numbers of older men, but it doesn’t happen in the absence of other problems.
How is ED diagnosed?
Diagnosis is usually done by a physician using several of the following sources of information:
Medical history – Any evidence of illnesses or even a recollection of sexual activity can help a physician determine where the problem is coming from.
Physical exam – Pain in the penis may suggest a nerve issue, where hormonal problems may show up as increased male breast size or abnormal hair growth. Circulatory problems may show up as decreased pulse in the wrists and/or ankles. Peyronie’s disease may cause impotence by causing the penis to bend to the point of making it difficult to maintain an erection.
Psychological exam – Interviews and questionnaires can reveal the mental aspects that may be contributing to the problem. A man’s partner may also be helpful in explaining what the problems might be in this area.
How is ED treated?
Luckily for most men, ED is a curable condition. A number of different treatments are available that can make a real difference, even completely reversing the effects. Physicians typically suggest treatments starting with the least invasive, moving up to higher-risk options only after all the low-risk options have been attempted.
If, for example, you suspect that the heart medication you are taking is the problem, telling your doctor may result in his trying a different class of medicine or altering the dosage. Some patients may be suited to have psychotherapy or behaviour modifications. Others may try using herbal medicines next, as they don’t typically conflict with other medications, and have a high rate of effectiveness.
Oral drugs (like Viagra) are often considered next, followed by locally injected drugs. Vacuum devices are often the next step, followed by surgery as a last resort after all other methods have been tried. The dangers involved with surgery make it a last resort.
A viable option (and highly successful in many cases) is treatment with herbal combinations. In clinical testing, several herbal ingredients have been proven highly effective against mild to moderate cases of ED, with clinical results showing as much as 90% effectiveness in treating erection problems. One source of these ingredients can be found at the following website: Sexy Stuff Shop




